In order to create an impeccable eCommerce App for Magento 2, you need to use the best testing methods. Not sure which ones? We’ll help you out. But first, a word on eCommerce and its importance.
Electronic commerce is the trading in goods or services via the Internet. Nowadays, eCommerce is developing by leaps and bounds. According to some statistics, about half of all Internet users purchase products online. In the future, this figure is expected to grow even more. This fact drives the business all over the world to enter the online trading market.
Magento 2
Most organizations use Magento 2 since it’s a powerful and multifunctional eCommerce platform for building online stores. Due to its modular architecture and flexibility, this eCommerce platform is very popular. It is suitable for all small, medium, and large companies since it is flexible and able to grow with business when it becomes huge.
Moreover, a wide range of functions helps Magento win customers worldwide. This platform is used in all parts of the world but mainly in North America and Australia.
Advantages of Magento 2
Magento has gained its popularity for a number of reasons:
- A stable system with regular updates that cover issues appearing in the system
- Possibility to create multiple stores in one control system
- Multilingual system
- Marketing & Promotional Tools
- Free Community Edition that gives the user an opportunity to try Magento before purchasing it
- Search Engine Optimization Tools
- User-friendly and intuitive administration interface
- Effective report system
- Easily integrated with Google services
- A huge number of extensions
Disadvantages of Magento 2
Of course, just like any other system, Magento too has some drawbacks:
- Performance (good hosting is required)
- Magento customizing is rather complicated
- Enterprise Edition is expensive
- Many extensions lead to a great number of bugs
Setting up Magento 2
During the setup process, it is advisable to pay attention to:
- Performance
- Compatibility of extensions
- Payment methods
- Shipping methods
- Responsive design
Testing Magento eCommerce Applications
The more functions a platform provides, the more vulnerable it is. Therefore, thorough testing is vital for Magento eCommerce applications to prevent end-users from facing defects and errors. It is very important to organize the testing process properly since this will ensure the customers’ ability to make online purchases quickly and easily.
Testing Tips
Following testing tips are pieces of advice to be used:
- Provide cross-browser and mobile testing (front-end testing on various browsers and mobile devices).
- Check that every installed extension is compatible with other extensions (make sure that a plugged-in extension works properly, provide regression testing for extensions with similar or connected functionality; one extension can cause a problem in another one).
- Carry out performance testing (check the application under a heavy load and a large amount of data to be sure that a great number of orders won’t make your online store go down).
- Check every payment method (calculation should be correct and the payment process should be clear to the customer).
- Double-check calculation on checkout and basket pages (especially with vouchers, promotions, and gift cards).
- Automate typical workflows (recommended to run after every change; helps detect problems in the early stages).
Magento offers a lot of possibilities for starting or growing online business and satisfying end-users’ needs. In order for e-business to work right and bring profit, you’ll need a sound approach to setting up and testing apps. Improvement testing is one of the key goals in Magento. It enables code quality boosting and finds introduced bugs earlier. What is more, it reduces release overheads by making more frequent releases possible, and so on.
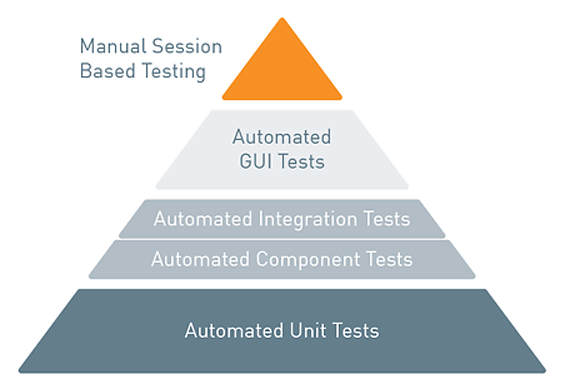
Testing Types
There are 3 major groups of testing:
- Unit Testing
- Integration Testing
- Functional Testing
They all have their goals, so you should know their major features to choose the most suitable for your issue.
Unit Testing
The first major software testing method is Unit Testing. Its main goal is to determine if individual parts of source code and different sets of program modules work correctly. This method relies on units as the smallest testable parts of an application. A unit could be an individual function, an entire module, or an interface.
Unit test can be used for:
- finding problems in the development cycle;
- allowing code refactoring at a later date;
- reducing uncertainty in the units;
- a bottom-up testing approach;
- sorting a system’s living documentation.
Integration Testing
Integration Testing is a continuation of the previous method. Individual software modules (after being tested separately) are combined and tested as a system. Thanks to this method, you can find out whether the system is ready for validation testing or not.
The major types of integration testing are:
- Big Bang – Major parts of the system or complete software systems are tested;
- Bottom-Up – Testing starts from the lowest level components to higher-level components;
- Top-Down – The top integrated modules are tested first and the branch of every module is tested gradually until the end of the related module;
- Sandwich – It combines Top-Down and Bottom-Up Testing.
Functional Testing
The third method is Functional Testing, a process of quality assurance based on the specifications of the software component that is being tested. It consists of two major parts: feeding the input and examining the output. Also, it describes what the system can do and rarely considers the internal program structure.
Functional testing consists of:
- functions identification
- input data creation
- output determination
- test case execution
- expected and actual outputs comparison
- troubleshooting
JavaScript Tests
Apart from these major groups, there are plenty of other tests. JavaScript in websites started small but has grown into large scale libraries. JavaScript is a programming language, and so testing of JavaScript is equally as valid as other tests.
Automated Tests in Magento
An eCommerce entrepreneur must follow the market changes in today’s competitive retail industry. Also, they have to make regular modifications to the website. These small changes make it possible for an online store owner to keep up with the latest trends. Moreover, these enable store owners to stay competitive. The mentioned changes may include new products, offers, discounts, shipping/payment methods, etc.
Companies must ensure a ‘flawless’ user experience during regular modifications and avoid undesirable results. So, QAs must continuously check the website and make sure to remove all the errors.
Cons of Manual Testing
Usually, Web development companies work according to an agile methodology. In other words, the ‘sprints’ are quite short and it is necessary to run comprehensive regression tests after each modification. Unfortunately, when changes are too often, manual testing may become monotone and may take a lot of time.
Sooner or later, you will have to apply some sort of ‘facilitation’. This may very much facilitate the life of testers. Tests are developed quickly, but still in an optimal way, which can be quite cost-effective.
Advantages of Automated Tests
The introduction of automated tests has countless advantages. Here are some of them:
- The possibility of repeatedly replaying the test cases
- Test cases can be performed simultaneously
- Tests can be run without supervision
- Increased accuracy and greatly reduce errors generated by people
- Automation saves time and money
Tips for Testing Magento Extensions
Make sure to prepare test scenarios for:
- the installation process
- functionalities of the features mentioned in the documentation
Installation Testing
We have to install the extension with the various Magento 2 versions supported by the extension provider. The installation should pass as a root user as well as a non-root user. Afterward, we need to configure the settings as mentioned.
Functional Testing
We have to test the features as mentioned in the features list. Firstly, test the positive scenarios first and confirm the extension is working as expected. Then, test the negative scenarios. Confirm if the extension is able to handle various scenarios with appropriate alert messages.
Integration Testing
Once the extension passes installation and functional testing, integration testing has to be conducted. It is crucial to confirm if the extension’s functionality affects the site’s core features. These might include the Product listing page, shopping cart, checkout flows, or any third-party APIs and custom modules specific to the site.
Automated Extension Testing
Write automation scripts for the functional flows. Not only will it help test the extension in different Magento versions but also reduce the testing time.
Scripts should cover the following aspects:
- The business scenarios of the extensions.
- Confirm if the integration of the extension works as intended. For example, based on the configuration, the feature in the admin back end should be reflected in the site’s front end. Similarly, when we perform the transaction in the site’s front end, it should be stored in the admin.
- Adding a new extension should not affect Magento’s default varnish caching mechanism. In other words, cacheable pages like CMS pages should appear from the cache.
Test Documentation
Upon the project completion, the following test artifacts should be provided:
- The Quality Report with the description of all defects. These should be sorted by their priority, as well as by devices and functional modules of the application in which they were detected.
- Detailed issues listed in a bug-tracking system. These should include screenshots and video clips.
- Report on the performance testing results
- Structured recommendations on the system environment and app quality improvement
Conclusion
Hopefully, you will find these tips for testing Magento 2 eCommerce applications useful. In case you have any questions on Web and Magento development, feel free to contact us at [email protected]
